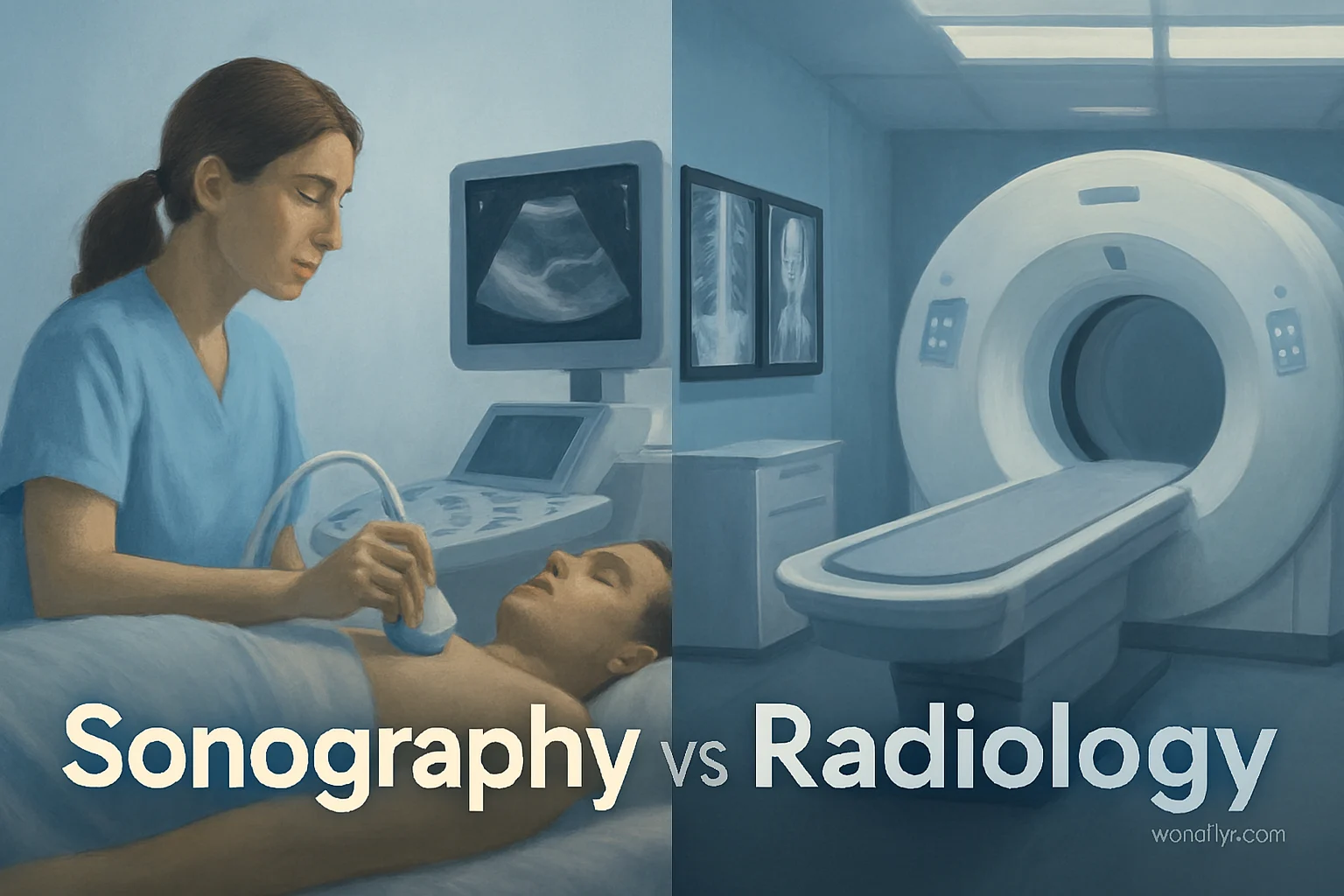
Introduction
If you’ve ever visited a hospital or diagnostic center, you’ve probably heard the terms sonography and radiology used interchangeably. Many patients assume they mean the same thing because both involve medical imaging and diagnostics. Even students entering the healthcare field often confuse these two paths when choosing a career.
The confusion makes sense. Sonography is closely linked to radiology, and both play a crucial role in diagnosing illnesses without surgery. However, their scope, techniques, and responsibilities are not the same.
Although they look/sound similar, they serve completely different purposes.
In this in-depth guide on sonography vs radiology, we’ll explain what each field actually is, how they differ, where they overlap, and which one might be right for patients or future medical professionals. By the end, you’ll clearly understand the distinction—no medical jargon overload, just clear explanations.
What Is Sonography?
Sonography, also known as ultrasound imaging, is a medical imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to create images of structures inside the body.
Clear Meaning
Sonography is a non-invasive diagnostic method that captures real-time images of organs, tissues, and blood flow using sound waves instead of radiation.
How It’s Used
Sonography is commonly used to:
- Monitor pregnancy and fetal development
- Examine organs like the liver, kidneys, and gallbladder
- Evaluate blood flow using Doppler ultrasound
- Detect cysts, tumors, or fluid buildup
It is especially valued because it is safe, painless, and radiation-free.
Where It’s Used
Sonography is used worldwide in:
- Hospitals
- Diagnostic imaging centers
- Maternity clinics
- Emergency departments
There are no regional grammar differences, as sonography is a medical term used consistently across countries.
Examples in Sentences
- “The doctor ordered a sonography to check the abdominal pain.”
- “Pregnancy sonography helps monitor fetal growth.”
- “She trained as a diagnostic medical sonographer.”
Short Historical or Usage Note
Sonography became widely used in medicine during the 1950s, initially for obstetrics. Over time, it expanded into cardiology, vascular studies, and general diagnostics. In the sonography vs radiology discussion, sonography is known for being specialized and patient-interactive.
What Is Radiology?
Radiology is a broader medical specialty that uses medical imaging technologies to diagnose and sometimes treat diseases.
Clear Meaning
Radiology is a medical field that includes multiple imaging techniques such as:
- X-rays
- CT scans
- MRI
- Fluoroscopy
- Nuclear medicine
- Ultrasound (sonography)
How It’s Used
Radiology is used to:
- Detect fractures, tumors, infections, and internal injuries
- Guide minimally invasive procedures
- Monitor disease progression
- Support treatment planning
Radiologists are medical doctors who interpret images and provide diagnostic reports.
Where It’s Used
Radiology departments exist in:
- Hospitals
- Trauma centers
- Oncology units
- Specialized imaging clinics
The term radiology is globally standardized in medical practice.
Examples in Sentences
- “The patient was referred to radiology for a CT scan.”
- “Radiology plays a key role in cancer diagnosis.”
- “He is specializing in interventional radiology.”
Regional or Grammatical Notes
Radiology includes sonography, but not all radiology involves sonography. This distinction is critical in understanding sonography vs radiology.
Key Differences Between Sonography and Radiology
The main difference in sonography vs radiology lies in scope, training, and technology used.
Quick Difference Summary
- Sonography uses sound waves only
- Radiology uses multiple imaging technologies
- Sonographers are imaging specialists
- Radiologists are licensed medical doctors
- Radiology includes sonography, but sonography does not include all radiology
Comparison Table: Sonography vs Radiology
| Feature | Sonography | Radiology |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Ultrasound imaging technique | Medical imaging specialty |
| Technology Used | Sound waves | X-ray, MRI, CT, ultrasound |
| Radiation Exposure | None | Often yes (except ultrasound/MRI) |
| Practitioner | Sonographer | Radiologist (MD) |
| Scope | Narrow and specialized | Broad and comprehensive |
| Real-Time Imaging | Yes | Sometimes |
| Patient Interaction | High | Limited |
This table clearly highlights why sonography vs radiology is not a matter of similarity but of hierarchy and scope.
Real-Life Conversation Examples
Dialogue 1
A: “Is sonography the same as radiology?”
B: “Sonography is actually part of radiology.”
A: “Oh, so radiology is bigger?”
B: “Exactly.”
🎯 Lesson: Radiology is the broader field.
Dialogue 2
A: “Why didn’t they use X-rays during pregnancy?”
B: “They used sonography instead—it’s safer.”
🎯 Lesson: Sonography avoids radiation.
Dialogue 3
A: “Who reads my ultrasound report?”
B: “A radiologist reviews it.”
🎯 Lesson: Sonographers capture images; radiologists interpret them.
Dialogue 4
A: “Can a sonographer diagnose diseases?”
B: “No, only radiologists can diagnose.”
🎯 Lesson: Diagnosis comes from radiology doctors.
Dialogue 5
A: “Should I study sonography or radiology?”
B: “Sonography is technical; radiology is medical school-based.”
🎯 Lesson: Career paths differ significantly.
When to Use Sonography vs Radiology
Understanding sonography vs radiology is especially useful in medical decisions and career planning.
Use Sonography When:
- Monitoring pregnancy
- Checking soft tissues and organs
- Evaluating blood flow
- Radiation exposure must be avoided
Memory Trick:
Sono = Sound = Safe
Use Radiology When:
- Diagnosing fractures or trauma
- Detecting cancer or internal bleeding
- Performing image-guided procedures
- Comprehensive diagnostic evaluation is needed
Memory Trick:
Radio = Range of imaging tools
US vs Global Practice
- In the US, sonographers require certification, while radiologists attend medical school
- Globally, radiology standards are consistent, but sonography training varies
This distinction often comes up in sonography vs radiology discussions.
Fun Facts or History
1. Ultrasound Was Inspired by Sonar Technology
Sonography evolved from sonar systems used in submarines during World War II.
2. Radiology Began with X-Rays in 1895
Wilhelm Röntgen’s discovery of X-rays laid the foundation for modern radiology.
Conclusion
The difference between sonography vs radiology is clearer once you understand their roles. Sonography is a specialized imaging technique that uses sound waves to safely visualize the body in real time. Radiology, on the other hand, is a broad medical specialty that includes many imaging technologies, including sonography itself. Both are essential to modern healthcare, but they serve different purposes, require different training, and answer different medical questions. Next time someone uses these two words, you’ll know exactly what they mean!