Introduction
If your dentist has ever mentioned a crown or a bridge, you’re not alone in feeling confused. These two dental terms are often discussed together, look somewhat similar in function, and are both used to restore damaged or missing teeth. Because of that, many patients assume they’re basically the same thing—or that one is just a fancier version of the other.
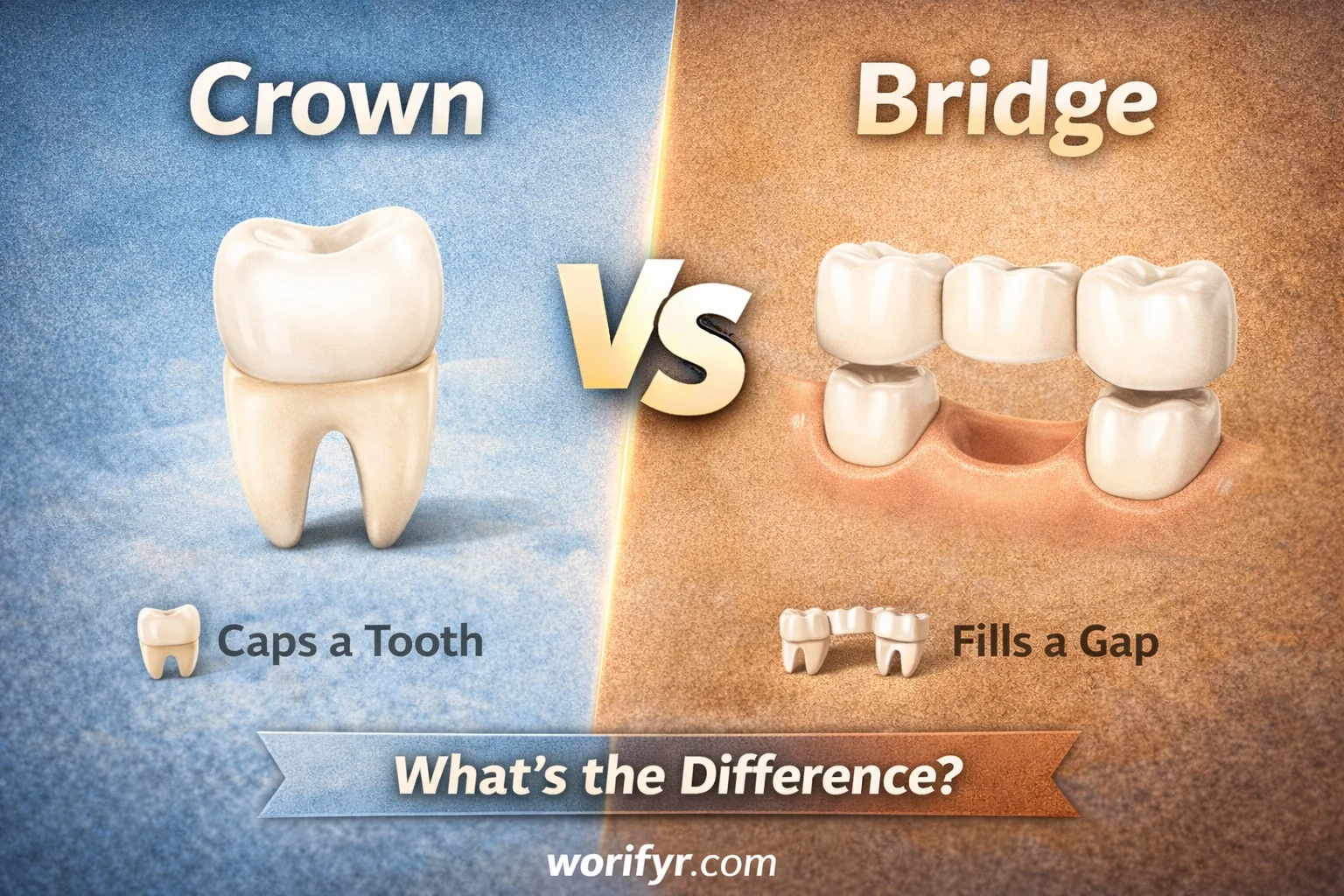
Although they look/sound similar, they serve completely different purposes.
Understanding the difference between crown vs bridge is essential before making a dental decision that affects your comfort, appearance, oral health, and budget. In this guide, we’ll break everything down in simple language: what each option is, how it works, when it’s used, and which one may be best for your situation. By the end, you’ll feel confident discussing your options with your dentist.
Section 1: What Is a Crown?
Clear Meaning
A dental crown is a cap that fully covers a damaged, weak, or treated tooth. Its main job is to restore the tooth’s shape, strength, and appearance.
In the crown vs bridge comparison, a crown is used when the tooth root is still present and can support restoration.
How It’s Used
A crown is placed over a natural tooth (or a dental implant) after it has been reshaped. Dentists commonly recommend crowns when a tooth:
- Is badly decayed
- Is cracked or broken
- Has had a root canal
- Is worn down
- Needs cosmetic improvement
Once cemented, the crown functions just like a natural tooth.
Where It’s Used (Dental Context)
Crowns are used worldwide and are a standard part of restorative dentistry in:
- The United States
- The UK
- Europe
- Asia
- Global dental practices
There are no regional differences in meaning—only material preferences.
Examples in Sentences
- “I need a crown after my root canal.”
- “The dentist placed a porcelain crown on my molar.”
- “A crown protects the tooth from further damage.”
- “In the crown vs bridge decision, I still had my tooth.”
Short Historical or Usage Note
Crowns date back thousands of years. Ancient civilizations used gold and shells to cover damaged teeth. Modern crowns now use porcelain, ceramic, zirconia, or metal alloys, making them stronger and more natural-looking than ever.
Section 2: What Is a Bridge?
Clear Meaning
A dental bridge is a restoration used to replace one or more missing teeth. It literally “bridges” the gap left by missing teeth using artificial teeth supported by neighboring natural teeth or implants.
In the crown vs bridge comparison, a bridge is used when one or more teeth are missing entirely.
How It’s Used
A traditional bridge consists of:
- Two crowns placed on healthy teeth (abutment teeth)
- One or more pontics (false teeth) in between
The supporting teeth are reshaped to hold the crowns, which anchor the bridge securely in place.
Where It’s Used
Dental bridges are commonly used in:
- General dentistry
- Cosmetic dentistry
- Restorative dentistry
They are globally accepted and used in both public and private dental systems.
Examples in Sentences
- “I got a bridge to replace my missing tooth.”
- “A dental bridge helped restore my smile.”
- “The dentist suggested a bridge instead of implants.”
- “In crown vs bridge cases, missing teeth usually mean a bridge.”
Regional or Usage Notes
There are different types of bridges—traditional, cantilever, Maryland, and implant-supported—but the core purpose remains the same: replacing missing teeth.
Key Differences Between Crown vs Bridge
Quick Bullet Points
- A crown covers an existing tooth
- A bridge replaces missing teeth
- Crowns restore strength and shape
- Bridges restore gaps in the smile
- Crowns use one tooth or implant
- Bridges rely on multiple teeth
Comparison Table (Mandatory)
| Feature | Crown | Bridge |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Covers damaged tooth | Replaces missing teeth |
| Teeth Required | One tooth or implant | Two or more teeth |
| Tooth Removal | No missing tooth needed | Missing tooth required |
| Structure | Single cap | Multiple connected units |
| Longevity | 10–15+ years | 10–15 years |
| Impact on Adjacent Teeth | Minimal | Requires reshaping neighbors |
| Cost Range | Lower | Higher |
| Complexity | Moderate | More complex |
Real-Life Conversation Examples
Dialogue 1
Patient: “Do I need a crown or a bridge?”
Dentist: “You still have the tooth, so a crown will work.”
🎯 Lesson: Crowns are used when the tooth still exists.
Dialogue 2
Patient: “Why can’t I get a crown here?”
Dentist: “There’s no tooth left—this calls for a bridge.”
🎯 Lesson: Missing teeth require bridges.
Dialogue 3
Patient: “Is a bridge stronger than a crown?”
Dentist: “They serve different purposes, not strength levels.”
🎯 Lesson: Function matters more than comparison.
Dialogue 4
Patient: “Why are my side teeth being reshaped?”
Dentist: “They’ll support the bridge.”
🎯 Lesson: Bridges rely on neighboring teeth.
When to Use Crown vs Bridge
Use a Crown When:
- Your tooth is cracked or decayed
- You’ve had a root canal
- The tooth structure still exists
- You want to preserve natural teeth
- Cosmetic correction is needed
Memory Trick:
👉 Crown = Cap the tooth
Use a Bridge When:
- One or more teeth are missing
- You want a fixed (non-removable) solution
- Implants aren’t an option
- You want quick gap restoration
- Neighboring teeth are healthy
Memory Trick:
👉 Bridge = Fill the gap
US vs UK Dental Usage
There is no difference in meaning or usage between US and UK dentistry for crown vs bridge. The terms are universal in dental care.
Fun Facts or History
1️⃣ Crowns Aren’t Always White
While porcelain crowns are common today, gold crowns are still used for durability—especially on back molars.
2️⃣ Bridges Prevent More Than Gaps
Bridges don’t just restore smiles—they help prevent teeth from shifting, which can cause bite problems and jaw pain.
Conclusion
The difference between crown vs bridge comes down to one simple question: Is the tooth still there? A crown is used to protect and restore an existing tooth, while a bridge replaces one or more missing teeth by anchoring to nearby teeth. Both are proven, effective dental solutions with long-term benefits when used correctly. Understanding these differences helps you make informed decisions about your oral health and treatment options. Next time someone mentions crowns and bridges, you’ll know exactly what they mean!